China’s Three Gorges Dam: Controversy and Achievement
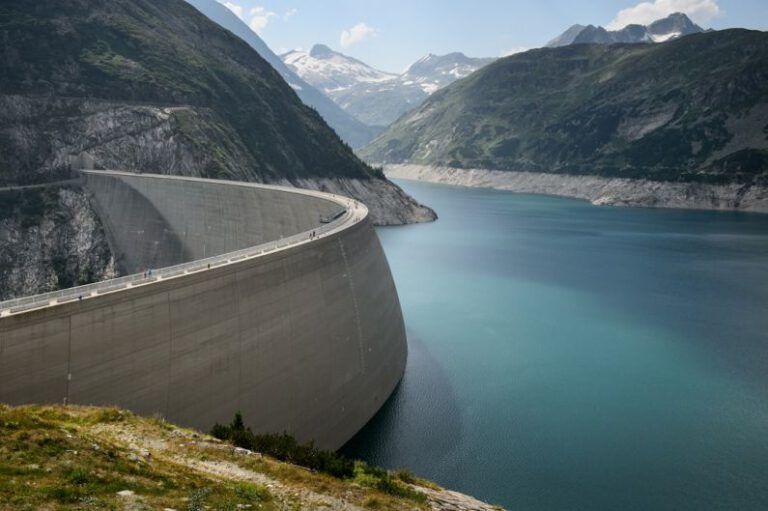
The Three Gorges Dam, located on the Yangtze River in China, is one of the largest and most controversial hydroelectric projects in the world. Spanning over a length of 2.3 kilometers and rising 185 meters above sea level, the dam has been a symbol of China’s engineering prowess and ambition since its completion in 2006. However, behind the facade of this monumental achievement lies a tapestry of controversies and environmental concerns that have sparked debate both within China and internationally.
The Engineering Marvel
The construction of the Three Gorges Dam was a monumental feat of engineering, requiring the relocation of over 1.3 million people and the flooding of 13 cities, 140 towns, and 1,350 villages. The dam’s primary purpose was to generate electricity, with a total capacity of 22,500 megawatts, making it one of the largest hydroelectric power stations in the world. The dam’s reservoir, which stretches over 660 kilometers, has helped control flooding along the Yangtze River, a region prone to devastating floods throughout history.
Environmental Impact and Controversies
Despite its achievements, the Three Gorges Dam has been a subject of intense controversy due to its environmental impact and social consequences. The dam has led to the displacement of millions of people, causing widespread social upheaval and loss of cultural heritage. The environmental impact of the dam has been significant, with concerns raised about increased seismic activity in the region, loss of biodiversity, and the disruption of the Yangtze River’s ecosystem.
One of the most contentious issues surrounding the dam is its impact on water quality. The reservoir behind the dam has become a repository for industrial and domestic waste, leading to pollution and degradation of water quality. The dam has also disrupted the natural flow of the river, affecting fish migration and sediment transport, which has had far-reaching consequences for the region’s ecosystem.
In addition to environmental concerns, the Three Gorges Dam has also faced criticism for its financial cost and economic viability. The project was plagued by cost overruns and delays, with the final price tag exceeding initial estimates by billions of dollars. Critics argue that the economic benefits of the dam have been overstated, with some experts questioning the long-term sustainability of the project.
Achievements and Legacy
Despite the controversies surrounding the Three Gorges Dam, it remains a symbol of China’s engineering prowess and ambition on the world stage. The dam has played a crucial role in meeting China’s growing energy needs, providing clean and renewable electricity to millions of people. It has also helped mitigate flooding along the Yangtze River, protecting communities from the devastating impact of seasonal floods.
The legacy of the Three Gorges Dam is a complex one, reflecting the trade-offs inherent in large-scale infrastructure projects. While the dam has brought tangible benefits in terms of electricity generation and flood control, it has also come at a significant cost to the environment and local communities. As China continues to grapple with the challenges of sustainable development, the Three Gorges Dam stands as a stark reminder of the complexities involved in balancing economic growth with environmental protection.
In conclusion, the Three Gorges Dam is a testament to human ingenuity and ambition, but it also serves as a cautionary tale about the unintended consequences of large-scale development projects. The controversies surrounding the dam highlight the need for careful consideration of the social, environmental, and economic impacts of such projects, as well as the importance of engaging with local communities and stakeholders in the decision-making process. As China looks to the future, the legacy of the Three Gorges Dam will continue to shape debates about development, sustainability, and the role of large infrastructure projects in achieving national goals.